|
The Kingdom 753-510
753 Romelus and Remus
found Rome according to the tradition.
642-617Roman territory reaches the coast during
the reign of Ancus Martius.
616 With the accession of Tarquinius Priscus to
the throne a period of strong Etruscian influence begin, it will not cease
until the creation of the republic 509. During this period Rome also take
over the position as Latium’s leading city from Alba Longa.
578-535 According to the tradition king Servius
Tullius reforms the military and creates the administrative division of Rome
into tribus.
510 This year is the traditional date for the
expelling of the last Roman king. A republic replaces the kingdom the
following year.
The Early Republic 509-367
507 The Etruscan king Porsenna seize Rome. He
is defeated three years later by a coalition of Latins and Greeks from the
city of Kyme.
498-493 The Latin War, Rome is forced to recognise
the Latin cities autonomy, which in their turn only recognises Rome’s
leadership in times of war.
494 The plebeians migrate to the sacred mountain
and return to Rome only after the patricians make concessions to them. The
office of popular tribune is thereby created to protect the plebeians’
interests.
471 Concilium plebis, a popular assembly for the
plebeians is created. It will later evolve into the comitia tributa, which
also includes patricians.
450 The laws are written down on twelve public
tables.
449 A new migration by the plebeians lead to the
revocation of the law against marriages between patricians and plebeians.
The same year Rome defeats the Italic tribe of the Sabines.
406-396 The ten-year war against Veii, the
Etruscan city become Rome’s first large conquest.
387 The Gauls sack Rome (the traditional year is
390).
381 Rome’s neighbour city Tusculum is granted
Roman citizenship.
378-353 The eleven kilometres long Servius wall is
erected around Rome.
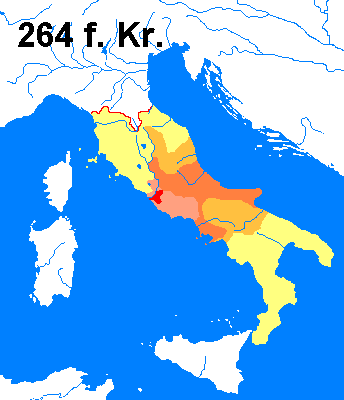 |
 = Rome 500 BC
= Rome 500 BC
 = Conquests to 338
= Conquests to 338
 = Conquests to 304
= Conquests to 304
 = Conquests to 290
= Conquests to 290
 = Conquests to 264
= Conquests to 264 |
The Middle Republic 367-133
367-366 The Licino-Sextian laws resolve the
class conflict between patricians and plebeians. The plebeians get access to
the highest offices and their leading families merge with the patricians
into a new upper class.
343-341 The First Samnite War ends with a
compromise, Capua is incorporated with Rome and the Samnites enter a union
with the Sidicines.
340-338 The Latin War, an insurrection against
Rome by the Latin cities is subjugated. Rome thereafter dissolves the Latin
league and ties the members to Rome with individual treaties. Campania,
which also took part in the insurrection, shares their fate.
326-304 The Second Samnite War, Rome is victorious
despite of a humiliating defeat at the Caudine Passes 321 BC, and annex
Campania.
312 The construction of Via Appia, the first major
Roman road, is completed.
300 Plebeians gets admission to religious offices.
Plebeians have thereby achieved legal equality with the patricians.
298-290 The Third Samnite
War, a coalition of Samnites, Sabines, Etruscans and Gauls challenge Rome’s
hegemony but are defeated. Central Italy is thereafter firmly under Roman
control.
287 A new migration by the plebeians result force
the patricians to recognise the decisions made by the plebeians’ popular
assembly as Roman laws.
285-282 War against the Gauls, Gallia Senones is
conquered.
282-272 War against Tarentum, which receive aid
from the Greek king Pyrrhus. He wins several "Pyrrhic" victories at Heraclea
280 and Ausculum 279. But he returns to Greece when the battle at Beneventum
275 ends in a tie. Tarentum submits to Rome 272 and is followed by Rhegion
270 whereupon all city states in southern Italy have become Roman client
states.
265 An insurrection by the Etruscan city Volsinii
is defeated.
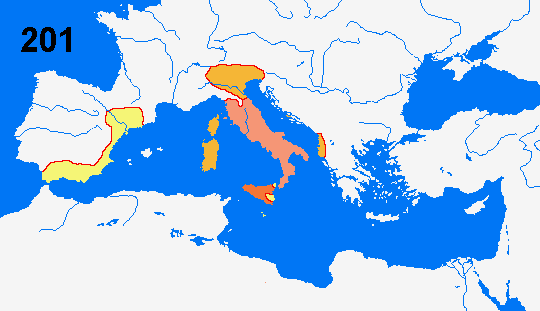
 = Roman Empire 264 BC
= Roman Empire 264 BC
 = Conquests to 241
= Conquests to 241
 = Conquests to 218
= Conquests to 218
 = Conquests to 201
= Conquests to 201
264-241 The First Punic War. When Rome sent
military aid to Messina against Syracuse in Sicily they provoked a war
against Carthage. The war was fought mainly at sea and resulted in the Roman
conquest of Sicily.
238 A mutiny among the soldiers in Sardinia and
Corsica forces Carthage to cede these islands to Rome.
229-228 The First Illyrian War, Rome eliminates
the Illyrian pirates and forces their queen Teuta to acknowledge Roman
supremacy.
227 Sicily becomes the first Roman province.
Sardinia and Corsica becomes the second province the same year.
226 Treaty between Carthage and Rome is signed,
the river Ebro becomes the border between their spheres of interests in
Spain.
222 The Celtic Insubre are defeated and Mediolanum
(Milan) is conquered whereby the province of Gallia Cisalpina is created.
219 The Second Illyrian War, Rome conquers a
foothold on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea.
218-201 The Second Punic War. Rome provokes a new
war against Carthage when they signed an alliance with the city of Sagentum
south of Ebro. The Carthagian commander Hannibal crosses the Alps with his
army and annihilates a Roman army at the battle at Cannae 216. But he fail
to win a decisive victory and is forced to return to Africa 203, there he
the year after is defeated in the battle at Zama. Rome conquers Syracuse and
Carthage’s territory in Spain.
215-205 The First Macedonian War. Macedonia
intervenes in the Second Punic War on Carthage’s side but fail to conquer
Illyria.
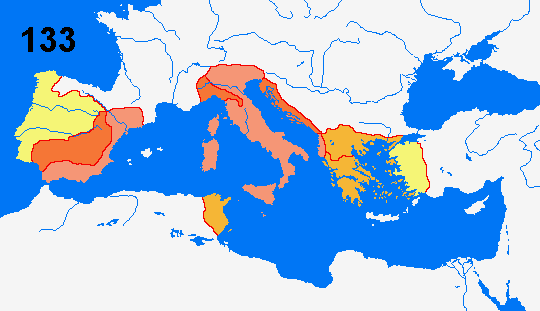
 = Roman Empire 201 BC
= Roman Empire 201 BC
 = Conquests to 167
= Conquests to 167
 = Conquests to 146
= Conquests to 146
 = Conquests to 133
= Conquests to 133
200-197 The Second Macedonian War. Pergamon,
Athens and Rhodes appeal to Rome for help against Macedonia. The Roman
consul Flamininius defeats the Macedonians in the battle at Kynoskefalai.
Rome takes over Macedonia’s hegemony over Greece.
200-190 Rome suppress an uprising by the Gauls in
northern Italy.
196 Flamininus declare the Greek states
independent under Roman protection at the Isthmian games.
192-188 War against the Seleucid Empire, whose
king Antiochus III tried to conquer Egypts possessions in Greece. Rome
defeats him and forced him to cede his possessions in Asia Minor to the
Roman allies Pergamon and Rhodes.
191-189 Revolt by the Iberians against Roman rule
over Spain.
171-168 The Third Macedonian War. Rome defeats the
Macedonians in the battle of Pydna 168 and partition Macedonia into four
republics.
167 Because of the huge booty from the Macedonian
war the Roman citizens were excused from pay war contributions. The Illyrian
king Genthios who had supported Macedonia is defeated the same year and his
kingdom is transformed into the Roman province of Illyricum.
166 Rome establish a free port at Delos, which
take over the trade from Rhodes.
154-133 A new uprising challenge Roman rule over
the Iberian Peninsula. After several defeats the Roman army led by Conelius
Scipio Aemilianus seize Numantia 133 whereby the spanish provinces are
finally pacified. The northwestern part of Spain will however remain
independent for another century.
149-146 The Third Punic War ends with the
destruction of the city Carthage and the complete conquest of the country,
which is transformed into the Roman province of Africa.
148 An insurrection in the Macedonian states is
crushed and Macedonia becomes a new Roman province.
146 A Greek insurrection against the Roman
hegemony results in the destruction of Corinth and that the country is
transformed into another Roman province.
135-132 The First Slave War break out when the
slaves in Sicily revolts. Rome crush the uprising and crucify 20 000 slaves.
133 King Attalos III of Pergamon bequeaths his
kingdom in Asia Minor to the Roman people.
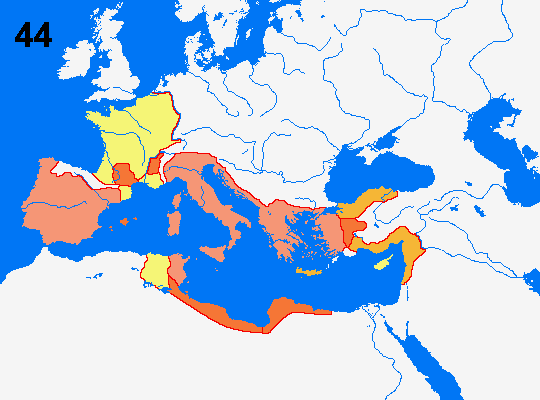
 = Roman Empire 133 BC
= Roman Empire 133 BC
 = Conquests to 96
= Conquests to 96
 = Conquests to 64
= Conquests to 64
 = Conquests to 44
= Conquests to 44
The Late Republic 133-31
133 Tiberius Gracchus who had proposed to
distribute public land to dispossessed peasants is murdered when he
illegally tries to be re-elected as popular tribune.
123 Tiberius brother Gajus Gracchus continues with
plans for land reform but let his slave kill him after that several of his
followers had been murdered during civil disturbances in Rome.
121 Parts of southern France are conquered by the
Romans and transformed into the province Gallia Transalpina, later Gallia
Narbonensis. The Balearic Islands are incorporated with Rome at the same
time.
113-101 War against the Cimbri and Teutones. The
consul Marius defeats the Germanic tribes who had migrated from Jutland to
southern Europe.
111-105 The war against Jugurtha of Numidia in
Africa is won by Marius.
107 As consul Marius carry out military reforms
and introduce a professional army.
104-101 A new uprising by slaves breaks out on
Sicily.
101 Cilicia on the southern coast of Asia Minor is
occupied by Roman troops in an effort to stamp out piracy.
100 Public disturbance in Rome break out again
when the popular tribune Saturnius proposes reforms in the spirit of the
Gracchus brothers.
96 Cyrenaica is bequeathed to Rome.
91-89 The Social War. Rome’s Italian allies revolt
and create their own state. Rome defeats the rebels but is forced to grant
them Roman citizenship.
88-84 The first war against Mithradates VI of
Pontus. Mithradates appeal to the Greeks to rise against Rome and massacre
80 000 Romans in Asia Minor. In Rome a conflict erupts over the leadership
of the army between Marius and Sulla. The latter wins but Marius take
control over Rome and terrorise Sulla’s supporters while he is occupied with
the successful campaigns against Mithradates.
83-81 In the second war against Mithradates Rome
forces him to acknowledge the terms concluded in the earlier peace treaty.
83-72 One of Marius supporters, Sertorius, revolts
in Spain. Pompey fights him but the revolt ends first when one of his
officers murder him.
82-79 Sulla return to Rome and take as dictator a
bloody revenge on Marius supporters.
74 King Nikomedes IV of Bithynia bequeaths his
kingdom to Rome.
74-64 The third war against Mithradates. After
initial successes the Roman army mutinies. Pompey take command of the army
66 BC and finish the war. Rome becomes the undisputed master of the eastern
Mediterranean and the provinces of Syria, Pontus and Cilicia are added to
the empire.
73-71 Slaves led by Spartacus revolts in Italy,
they are defeated by Crassus and Pompey.
67 Pompey exterminate piracy in the Mediterranean
and conquers Crete and Cilicia.
63-62 Cicero discovers and suppress as consul the
conspiracy of Cataline, 3 000 of Cataline’s supporters are killed.
60 Pompey, Crassus and Julius Caesar establish the
first triumvirate, together they control Rome and they distribute the
offices among themselves.
58 Cyprus is incorporated to the empire as a new
province.
58-51 The Gallic Wars, Julius Caesar conquers Gaul.
55-54 Julius Caesar leads two expeditions to
Britain.
54-20 The first war against the Parthians break
out when they declare war on the Roman client state Armenia. Crassus dies in
the disastrous battle at Carrhae 53. The Parthians invade Syria and Asia
Minor 40-38. Mark Antony’s campaign in Armenia 36 ends in failure. Augustus
conclude peace with the Parthians 20 BC whereby they recognise Roman
supremacy over Armenia and return the legion standards taken from Crassus
and Antony.
49-45 Julius Caesar crosses the river Rubicon and
start a civil war against Pompey and his supporters. Julius Caesar is
victorius and becomes dictator for life. Numidia becomes the Roman province
of Africa Nova 46 BC.
47 Mithradates son Farnakes tries to take back
parts of the kingdom of Pontus that had been conquered by Rome but Julius
Caesar defeats him in the battle at Zela (veni vidi vici).
44 Julius Caesar is murdered by a senatorial
conspiracy.
43 Mark Antony, Lepidus and Octavian form the
second triumvirate to avenge the murder of Julius Caesar and to reorder the
state.
42 Julius Caesar’s murderers are defeated at the
battle of Philippi.
36 Sicily, which is held by Pompey’s son Sextus,
is seized by Lepidus and Octavian’s right hand Agrippa. Lepidus then
challenges Octavian but his soldiers mutinies and joins Octavian.
34 Mark Antony accuse the Armenian king for not
giving him the promised support in the war against the Parthians and capture
him after a campaign in Armenia.
32 Rome declares war against queen Cleopatra of
Egypt. Mark Antony choose to fight on Cleopatra’s side.
The chronology continues on the page: The Imperial Age. |

