|
The Imperial Age
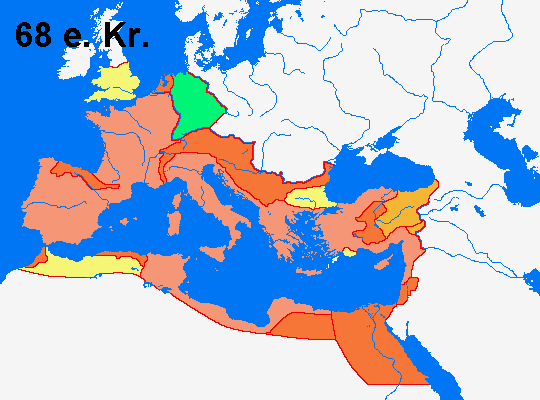
 = Roman Empire 31 BC
= Roman Empire 31 BC
 = Conquests to AD 14
= Conquests to AD 14
 = Conquests to 37
= Conquests to 37
 = Conquests to 68
= Conquests to 68
 = Temporary conquest 12 BC-AD 9
= Temporary conquest 12 BC-AD 9
The Julio-Claudian Dynasty 31 BC-AD 68
31 Octavian defeats Mark Antony in the battle
of Actium and become the sole ruler over Rome.
30 Octavian conquers Egypt.
29 Moesia in the Balkans is incorporated to the
Roman Empire.
27 Octavian formally surrender his special powers
to the senate. For that he receives the honorary title Augustus from the
Senate, which is the name he will be called by thereafter. In reality the
republic have been dissolved and replaced by an imperial regime because
Augustus retains control over the army, have the largest wealth and the
popular support.
26-25 Augustus wage war in Spain.
25 King Amyntas of Galatia in Asia Minor bequeaths
his kingdom to Rome. The same year an unsuccessful campaign against the
Arabs is carried through.
19 Agrippa subdue the last resistance against
Roman rule in Spain.
16-15 Augustusís stepsons Tiberius and Drusus push
the Roman frontier forwards the river Donau, Raetia become a Roman province
and the kingdoms Noricum and Thrace become Roman client states. The kingdoms
are later during Claudius reign incorporated to the Empire as provinces.
13-9 Pannonia is conquered by Agrippa and Tiberius.
12-9 Drusus conquers Germany to the river Elbe.
AD 6 The Roman client king Archelaos is deposed
and his kingdom is transformed into the Roman province of Judeae.
6-9 A serious insurrection in Pannonia requires
the effort of 15 legions to be subdued.
9 The Germans revolt and end Roman rule when they
annihilate three legions in the battle of the Teutoburger Forest.
14 Augustus dies and is succeeded by his adoptive
son Tiberius.
14-16 The Roman commander Germanicus tries to win
back Germany. But despite of some successes Tiberius aborts the attempt
because of excessive costs.
17-24 Tacfarinas leads a rebellion against Rome in
Numidia.
18 Cappadocia and commagene in Asia Minor are
incorporated with the Roman Empire.
22-31 The Praetorian prefect Sejanus have a large
influence over Tiberius. It leads to numerous trials, executions and
suicides among prominent Romans. Sejanus himself is executed when his
conspiracy against Tiberius is revealed.
37-41 Tiberius dies and is succeeded by Caligula
who soon becomes insane and struck by megalomania. He his murdered by the
Praetorian Guard 41 and succeeded by Claudius.
40-42 Caligula murder the Mauretanian king
Ptolemaios and annex his kingdom. The people there refuse to accept the
annexation and rise against the Romans who conquers the kingdom two years
later and divide it into two provinces.
43 Claudius conquers southern Britain and annex
Lycia et Pamphylia in Asia Minor.
46 Thrace become a Roman province.
54 Claudius dies and is succeeded by his adoptive
son Nero.
53-63 War against the Parthians over Armenia. It
ends with a compromise peace, the Parthians recognise Roman supremacy over
Armenia but a Parthian prince becomes its king.
60-61 The Britons lead by Queen Boudicca rises
against Rome. They are defeated after initial successes and Rome expands its
territory in Britain.
64 A fire destroys central Rome. Nero cast the
blame on the Christians who are persecuted.
65 A conspiracy against Nero is revealed, the
prominent philosopher Seneca is forced to commit suicide.
66-70 A serious revolt by the Jews in Palestine is
subdued by Vespasian and his son Titus.
68 Nero commits suicide when discontent with his
rule have led to mutinies in the army.
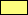
 = Roman Empire AD 68
= Roman Empire AD 68
 = Conquests to 96
= Conquests to 96
 = Conquests to 117
= Conquests to 117
 = Conquests to 199
= Conquests to 199
 = Temporary conquests
= Temporary conquests
The Flavian Dynasty 69-96
69 After Neroís death the legions appoint their
own generals as emperors and four of them succeed each others this year
until the Flavian dynasty seize the imperial throne with Vespasian.
69-70 The Batavians led by Civilis rises against
Rome in the Netherlands. The rebellion spreads to several Celtic and
Germanic tribes until it is defeated by the Romans.
70 The Jewish revolt is subdued when Titus seize
and destroy Jerusalem. Some pockets of resistance continue to fight the
Romans until 73 when the last of them commit collective suicide in the
Masada fortress.
71 Northern England is added to the Roman Empire.
74 The area between the rivers Rhine and Danube in
Germany (agri decumates) is conquered.
79 Titus succeeds his father Vespasian as emperor.
The cities Pompeii and Herculaneum are destroyed when the volcano Vesuvius
erupts.
79-84 Agricola conquers southern Scotland, but his
campaign is aborted after disturbances along the Danube frontier and the
conquest is thereafter abandoned.
80 Colosseum is inaugurated.
81 Titus dies and is succeeded by his brother
Domitian as emperor.
82-83 Domitian leads
a campaign against the Germanic Chatti and fortifies the border in Germany.
85-88 First Dacian War. Led by their king
Decebalus the Dacians in Romania challenge Romeís hegemony in the Danube
region.
89 The Germanic tribes Marcomanni and Quadi
invades Pannonia. A rebellion by the governor in Germania the same year
leads to incrising despotic rule by Domitian.
92 A new invasion is defeated by Domitian.
The Adoptive Emperors 96-192
96 Domitian is assassinated and the Senate
appoints the elderly senator Nerva as his successor. He adopts the general
Trajan and is succeeded by him when he dies 98.
101-102 The Second Dacian War, Trajan defeats
Decebalus.
105-107 The Third Dacian War, Decebalus does not
comply with the previous peace accord and Trajan conquers his kingdom.
106 The Nabatean kingdom is incorporated with the
Roman Empire as the province of Arabia.
113-117 War against the Parthians. Trajan conquers
Armenia and Mesopotamia.
117 Trajan dies and is succeeded by his adoptive
son Hadrian who immediately make peace with the Parthians by ceding Armenia
and Mesopotamia.
122-127 Hadrianís wall is erected along the
frontier in Britain.
132-135 A new rebellion by the Jews, their leader
Bar Kochba claims to be the messiah.
138 Hadrian dies and succeeds by his adoptive son
Antoninus Pius.
142 Antoninus Pius push the frontier forwards to
southern Scotland where the Antonine wall is erected.
161 Antoninus Pius dies and is succeeded by his
adoptive sons Marcus Aurelius and Lucius Verus.
161-166 War against the Parthians who occupies
Syria, Armenia and Cappadocia. Lucius Verus launches a successful counter
offensive and manage to occupy Mesopotamia until an outbreak of the plague
forces him to conclude peace with the Parthians.
167 A terrible plague that kills one quarter of
the Roman Empireís population culminates.
167-175 The First Marcomanni War. The Markomanni
and Quadi crosses Danube and invade northern Italy until Marcus Aurelius
manage to defeat them.
175 Avidius Cassius makes an unsuccessful attempt
to seize power in Rome.
178-180 The Second Marcomanni War. Marcus Aurelius
tries to secure the Empireís frontier by conquering the lands of the
Marcommani and their neighbours. But when he dies 180 his son and successor
Commodus abort the campaign and buy peace with the Germanic tribes.
184-185 Uprising in
Britain, the frontier is moved back to Hadrianís wall.
189 Civil disturbance in Rome when rivalry in the
bureaucracy causes a food shortage.
192 The incompetent Commodus who suffers from
megalomania is murdered in the bath on new years eve.
The Severan Dynasty 193-235
193 The second year of four emperors. Commodus
successor Pertinax is murdered by the Praetorian Guard, which sells the
office of emperor to the highest bidder. Didius Julianus wins the auction
but is not recognised by the legions, which instead appoint their own
generals as emperors. Septimius Severus wins the civil war the following
year and put the Severan dynasty on the imperial throne.
194-199 War against the Parthians. Northern
Mesopotamia is conquered and Roman supremacy over Osrhoene is restored.
195-197 Septimius Severus defeats Clodius Albinus
who claimed to be emperor.
208-211 An attempt to conquer Scotland is aborted
when Septimius Severus dies. He succeeds by his sons Caracalla and Geta.
212 Geta is murdered by Caracalla and give the
same year Roman citizenship to all free inhabitants in the Roman Empire.
213 Caracalla fights against the Alemanni, a
Germanic tribal confederation. Osrhoene becomes a Roman province.
216-218 Caracalla starts an unsuccesful war
against the Psrthians and his successor is forced to buy peace.
217 Caracalla is murdered Macrinus succeeds him.
He in turn is murdered only after one year and the Severan dynasty is
reinstated when Elagabalus becomes emperor.
222 Elagabalusís bizarre worship rituals to his
sun god make the Romans to turn against him and he is murdered. Elagabalus
is succeeded by his cousin Alexander Severus.
230-233 The Persians who 226 had taken over the
Parthian empire invades the Roman Empire. They capture Armenia 232 but
Alexander Severus repulses the attack.
231-235 The Alemanni invades Gaul. When Alexander
Severus tries to buy peace with them 235 his soldiers murder him. They
appoint Maximinus to emperor and he defeats the Alemanni the same year.
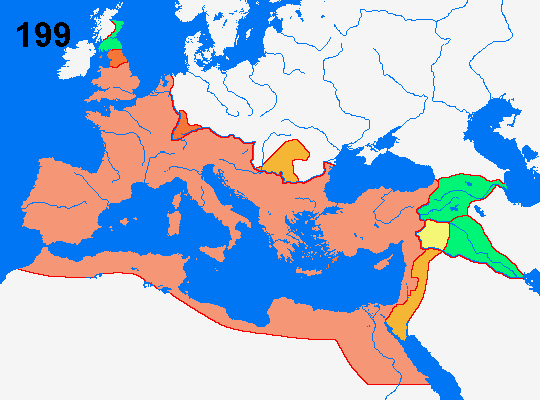
 = The Palmyrene Empire's (260-272) greatest extent 271
= The Palmyrene Empire's (260-272) greatest extent 271
 = The Gallic Empireīs (260-274) greatest extent 26
= The Gallic Empireīs (260-274) greatest extent 26
 = Permanent loss of territory
= Permanent loss of territory
The Barracks Emperors 235-284
236 Maximinus fights against the Sarmatians and
Dacians at the Danube.
237 The Persians invade and conquer Roman
Mesopotamia.
238 Maximinus is murdered during a conflict over
the throne and is succeeded by Gordian III. The Germanic Goths crosses the
Danube for the first time.
242 Gordian III defeats the Persians and take back
Mesopotamia.
244 Gordian III dies and is succeeded by Philip
the Arab who makes peace with the Persians by ceding Mesopotamia and the
supremacy over Armenia. Although it seems like the Roman troops remained
there and the war is continued a few years later.
246 Philip the Arab wards off an attack by the
Dacians.
249 Decius who was put in charge to handle an
attack by the Goths is proclaimed emperor by his soldiers and defeats Philip
the Arab. Decius starts the great persecutions against the Christians
because they are accused to have abandoned their old gods and thus caused
the crisis the Roman Empire is experiencing.
251 Decius is killed in battle against the Goths.
251-266 The Roman Empire is suffering from a new
great plague epidemic.
253 New attacks from the Persians who sack Antioch.
254 Valerian defeats his opponents and become
emperor. He goes to the offensive against the Persians. At the same time
Goths, Marcomanni, Quadi, Heruli and Sarmatians invade the empire.
254-256 Valerianís son and co-emperor Gallienus
lead several campaigns against the Alemanni and Franks along the Rhine.
256 The Goths are
ravaging the coast of Asia Minor.
259 The Alemanni invades northern Italy but
Gallienus defeats them. The same year he concludes peace with Marcomanni who
have ravaged the Balkans.
260 The Roman Empire is a state of dissolution
when the Persians invade and capture Valerian. The Franks ravage Gaul and
Spain. These parts of the empire together with Britain appoint their own
emperor (the Gallic Empire). Odenathus who rule over the semi-independent
city of Palmyra take charge of Syria and fights successfully back the
Persians. The persecutions against the Christians cease.
263 The Romans abandon the territory between the
rivers Rhine and Danube to the Alemanni.
267 Athens is sacked by the Heruli but Gallienus
defeat them on their way home. Gallienus is later murdered and Claudius II
succeeds him. He then fights back the attack on Northern Italy by the
Alemanni.
269 Claudius II defeats the Goths in the battle of
Naissus in present day Serbia. Spain defect from the Gallic Empire and is
returned to Romeís control.
269-271 Queen Zenobia (the widow of Odenathus)
attack the Roman Empire and conquers r Egypt and large parts of Asia Minor.
270 Vandals and Sarmatians attack Pannonia. The
Alemanni, Markomanni and Juthungi are pillaging the alpine region and
northern Italy. Claudius II dies of the plague and is succeeded by Aurelian
who then defeats the Juthungi.
271 The Alemanni and Juthungi are again pillaging
in northern Italy but Aurelian defeat them. The same year he orders the
construction of a new wall around the city of Rome.
272 Aurelian defeats Zenobia and return the
eastern provinces the Roman Empire. Dacia is however abandoned to the Goths.
274 The last Gallic emperor is defeated by
Aurelian and the unity of the Roman Empire is restored.
275-276 Aurelian is murdered and the senate
appoints Tacitus to his successor. He defeats the Goths in Asia Minor before
he dies of an unknown cause.
276-284 Continuos fighting against the Franks,
Alemanni, Burgundians, Vandals and Persians while emperors are getting
murdered until Diocletian ascend the throne and restore order.
.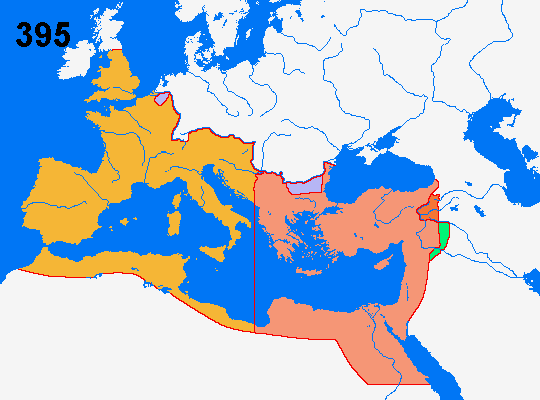
 = The West Roman Empire
= The West Roman Empire
 = The East Roman Empire
= The East Roman Empire
 = Germanic foederatis (Franks and Visigoths)
= Germanic foederatis (Franks and Visigoths)
 = Lost territory 363
= Lost territory 363
 = Gained territory 387
= Gained territory 387
The Late Empire 284-395
286 Diocletian appoints Maximian to co-emperor
with responisbility over the western half of the empire. Saxon and Frankish
pirates are ravaging in the English Channel. Carausisus revolt and is
proclaimed as emperor in Britain and later also in northern Gaul. The Romans
liberate Armenia from the Persians.
293 The Tetrarchy is introduced when two junior
emperors are appointed (Galerius and Constantius). They are each given
responsibility over a geographic area and are supposed to succeed the senior
emperors when they resign voluntarily. Constantius capture northern Gaul
from Carausius who is murdered and succeeded by Allectus as ruler over
Britain.
294 Diocletian fights against the Marcomanni,
Quadi and Sarmatians.
296 Constantius defeats Allectus and return
Britain to Romeís control.
296-298 War against Persia. Galerius defeats the
Persians and take back Mesopotamia. The border with Persia is thereby
secured for almost four decades.
297 Diocletian suppress an uprising in Egypt. The
same year he reorganises the empire into 101 smaller provinces grouped in 12
dioceses.
301 Price control is introduced to stop the
inflation, but it is thwarted by a growing black market.
303 Diocletian reintroduce the persecutions of the
Christians.
305 Diocletian and Maximian abdicates and is
succeeded by their junior emperors.
306-324 Disunity among the emperors leads to civil
wars, which not ends until Constantine the Great becomes the sole emperor
324.
308-309 Insurrection in the province of Africa.
313 The Milan edict of toleration end the
persecutions of the Christians and Constantine the Great favour them.
325 The council of Nicaea is called by Constantine
the Great to resolve theological disputes among the Christians, it condemns
Arianism.
330 Constantine the Great inaugurates
Constantinople, which become the capitol over the eastern half of the
empire.
336-363 War over Armenia against Persia. The
Persians conquer half of Roman Mesopotamia and win Armenia.
337 Constantine the Great is baptised on his
deathbed. His sons who soon start to fight against each otherís succeed him.
353 Constantius II becomes sole emperor and
favours arianism.
357-359 The Alemanni and Franks invade Gaul.
Julian the Apostate defeats the Alemanni in the battle of Argentoratum
(Strasbourg) and allows the Franks to settle in Belgium as Roman allies (foederati).
361 Julian the Apostate succeeds Constantius II as
emperor. He defects from Christianity and favours the pagan religions.
363 Julian is killed in a campaign against the
Persians and is succeeded by Jovian.
364 Jovian dies and is succeeded by Valentinian
who appoints his brother Valens to emperor over the eastern half of the
empire.
367 The Saxons who had conquered Britain is driven
away by the Romans.
369 An invasion by the Alemanni is repelled and
their homeland is ravaged by Romans and Burgundians.
372-375 An insurrection in Mauretania is
subjugated.
375 Valentinian defeats the Quadi who had invaded
Pannonia, but he dies shortly afterwards and he is succeeded by Gratian as
emperor in the west. Meanwhile the age of migrations starts when the Huns
arrive to Europe and subjugates the Ostrogoths north of the Black Sea.
376 The Visigoths migrate to the Roman Empire to
escape the Huns.
378 Romeís treatment of the Visigoths provokes a
war and they defeat a Roman army in the battle of Adrianople. Valens is
killed in the battle and his succeeded by Theodosius as emperor in the east.
380 Arianism is forbidden in favour of Catholicism.
382 Theodosius make peace with the Visigoths and
gives them right to settle in the Roman Empire as Roman allies (foederati).
387 Armenia is divided into a Roman and a Persian
sphere of interest, the Persians gets four quarters of the country.
390 Bishop Ambrosius forces Theodosius to repent
after he had ordered a massacre of 7 000 inhabitants in Thessasaloniki.
391 Paganism is
forbidden when Christianity becomes the state religion of the Roman Empire.
394 Theodosius ends the conflict over the throne
in the western half of the empire and becomes the sole emperor.
395 Theodosius dies and the Roman Empire is
divided for the final time in two halves when his sons succeed him.
The chronology continues on the page: The Fall of Rome. |

